Time to read: 6 min

Everything You Need to Know About Tensile Strength: A Comprehensive Guide by Unofactory
Tensile strength is a critical property of materials, particularly in the field of engineering and manufacturing. It is the measure of a material's resistance to breaking when subjected to pulling forces or tension. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about tensile strength, from its definition to its significance in material selection and quality control at Unofactory.
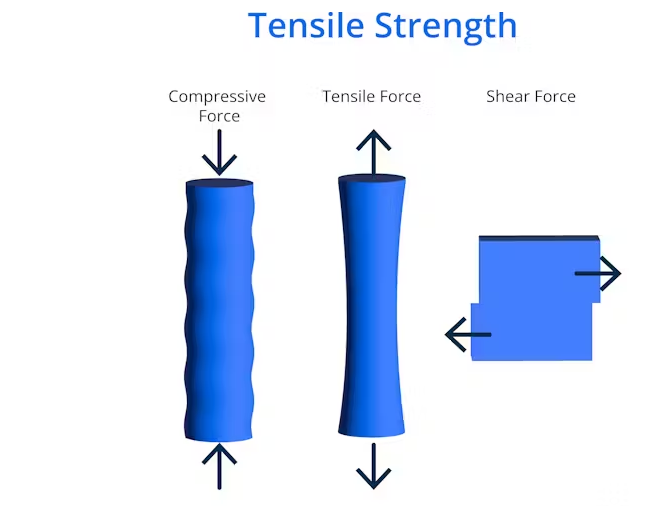
Understanding Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is defined as the maximum amount of tensile stress that a material can bear before breaking. It is an essential characteristic for evaluating the performance of materials under tension, which is a common mode of loading in many engineering applications. By understanding tensile strength, engineers can predict how a material will behave under stress and select the most appropriate material for a given application.
Importance of Tensile Strength in Material Selection
When choosing materials for a specific project, tensile strength is a key factor to consider. Materials with high tensile strength are more resistant to breaking and can withstand greater forces without failure. This is particularly important in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where the safety and durability of components are paramount.
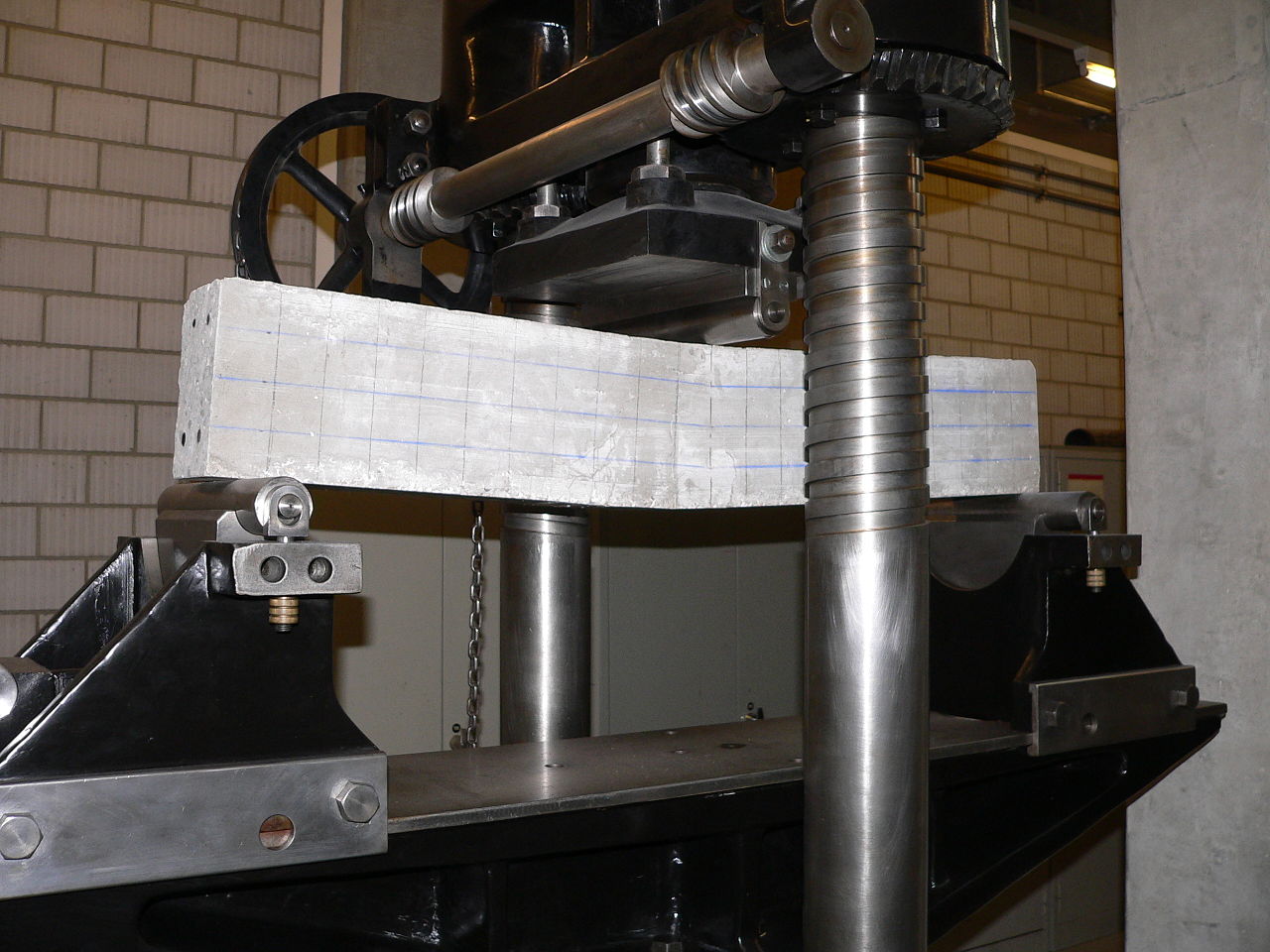
Tensile Strength Testing at Unofactory
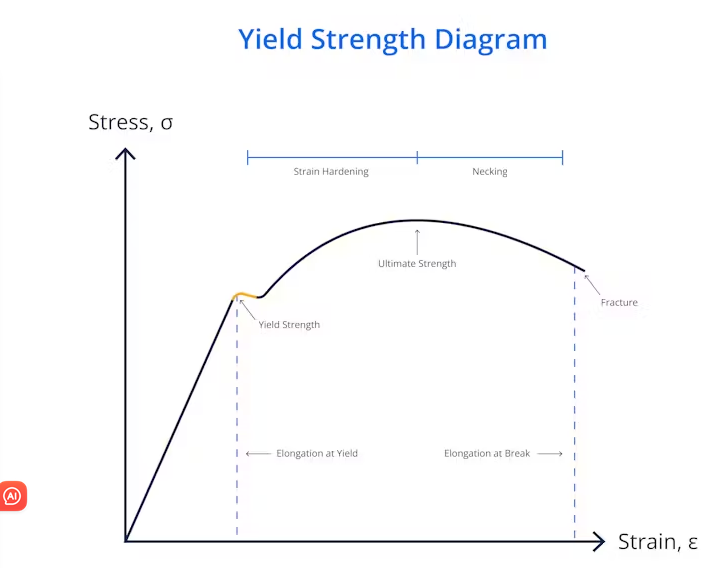
At Unofactory, we prioritize the quality and reliability of our products. Our state-of-the-art facilities are equipped to perform tensile strength tests on a variety of materials. These tests help us ensure that the materials we use meet the highest standards and are suitable for their intended applications.
Applications and Considerations
Tensile strength is not only important for the initial selection of materials but also for ongoing quality control. By regularly testing the tensile strength of materials, we can identify any inconsistencies or deviations from the expected performance. This allows us to maintain a high level of quality in our products and services.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tensile strength is a vital aspect of material science and engineering. It plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of materials for specific applications and ensuring the safety and longevity of engineered components. At Unofactory, we are committed to providing our clients with the highest quality products, and understanding and testing tensile strength is a key part of that commitment. For everything you need to know about tensile strength, and to ensure your projects are built on a foundation of strength and reliability, trust Unofactory.




