Time to read: 6 min
This comprehensive guide delves into the distinct characteristics of thermoset and thermoplastic polymers, offering a clear comparison to facilitate informed decisions in material selection for various industries. We explore their properties, applications, and the implications of choosing one over the other for your projects.
Introduction to Polymer Dynamics
In the vast spectrum of injection molding processes, thermoplastic polymers have been the go-to materials. However, the emergence of thermosetting plastics has introduced a new paradigm in the manufacturing sector. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for specific applications.
Understanding Thermoplastics
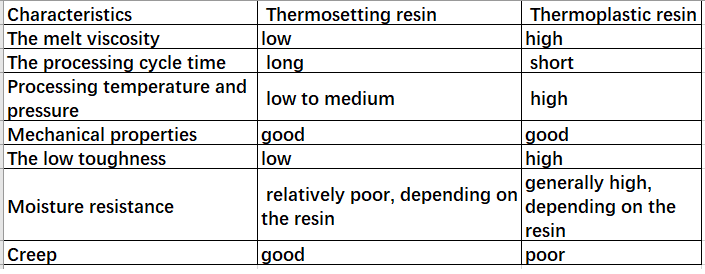
Thermoplastics are resins that remain solid at room temperature but soften upon heating, allowing them to be molded into various shapes. They can be melted and reshaped multiple times without altering their inherent properties, making them highly recyclable and suitable for processes like injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming.
Understanding Thermosets
In contrast, thermoset plastics start as liquid resins that harden upon heating or through chemical reactions, forming irreversible crosslinking bonds. Once cured, they maintain their shape and do not melt upon reheating, making them ideal for applications requiring high strength and heat resistance.
Key Differences Between Thermoplastics and Thermosets
- Melting Point: Thermoplastics have a lower melting point compared to thermosets, allowing them to be reshaped upon heating.
- Aesthetics: Thermoplastics are known for their high-quality finish, while thermosets offer unique opportunities for in-mold decoration, providing excellent adhesion and detailed textures.
- Corrosion Resistance: Thermoplastics generally exhibit higher resistance to chemical attacks than thermosets.
- Durability: Thermosets are more durable, offering better resistance to heat, corrosion, and mechanical creep, although they are non-recyclable.
Application Domains
Thermoplastics are widely used in industries such as medical, automotive, electronics, and construction for their versatility and recyclability. Thermosets, with their heat and chemical resistance, are chosen for electronic housings, chemical processing equipment, and automotive components.
Cost Considerations
While thermoplastics often present lower manufacturing costs, thermosets offer a balance of cost and performance, making them suitable for applications requiring complex geometries and high-temperature resistance.
Conclusion
The choice between thermoset and thermoplastic polymers depends on the specific requirements of your project. If heat resistance and durability are paramount, thermosets may be the ideal choice. However, for applications valuing recyclability and chemical resistance, thermoplastics could be more appropriate.
FAQs (Rewritten)
- What are the common uses of thermoplastics? Thermoplastics are commonly used in the production of belts, adhesives, pipes, insulators, and ropes, known for their recyclability and ease of reshaping.
- Are thermosets harder than thermoplastics? Yes, thermosets have a three-dimensional network of bonds making them stronger and more resistant to high temperatures than thermoplastics.
- Which material can better resist temperature, thermosets or thermoplastics? Thermosets can better resist high temperatures due to their strong covalent crosslinks, providing material stability.
UnoFactory Injection Molding Services
When selecting the right plastics for your products becomes challenging, UnoFactory is here to assist you. Our skilled engineers will analyze your design and recommend the optimal material choice, ensuring you receive the best service from our experienced team. With state-of-the-art machinery and competitive pricing, UnoFactory is your reliable partner for high-quality injection molded parts.
This rewritten article aims to provide a clear and concise comparison of thermoset and thermoplastic polymers, enabling readers to make informed decisions for their specific applications. If further details or customization are required, please specify.




